Pollen
Every plant has its specific pollen. Pollen is formed in pollen sacs, which are part of the stamen.
What is Pollen?
Every plant has its specific pollen. Pollen is formed in pollen sacs, which are part of the stamen. The stamen consists of a stalk that expands into an anther, which contains four elongated pollen sacs. When the anther fully matures, it opens, releasing millions of pollen grains. Each grain is a biological unit containing everything necessary for life.
Pollen grains of different plant species vary in shape, size, color, and taste. The type of plant determines the quantity of pollen grains. There are two groups of pollen grains based on size: anemophilous (wind-pollinated) and entomophilous (insect-pollinated). Wind-pollinated grains are smaller, lighter, and dry, transported by the wind. In contrast, insect-pollinated grains are rough and sticky, clinging to insects that pollinate flowers. Bees play a significant role in plant fertilization.
Harvesting Pollen
Beekeepers can collect about 10% of the pollen a hive gathers in a season without harming the bee colony’s development. A device with small openings, called a pollen trap, is placed at the hive entrance. Bees must pass through it, and about 60% of the pollen they carry falls off. This pollen, called “osmukane,” drops through a metal mesh into a collection container. Pollen can also be obtained by excavating it from honeycomb cells or within the honeycomb.
How Bees Collect Pollen
Bees visit only one type of flower during each flight, collecting pollen from that flower. When a bee lands on a flower, it gets covered in pollen. Bees have tiny, fluffy hairs covering their bodies, which help trap pollen grains. While in flight, bees clean themselves, moving pollen toward the lower abdomen or the rear legs, where they have special devices (baskets and brushes) to collect pollen. Younger bees in the hive, which haven’t started foraging yet, use their heads to push pollen into cells, minimizing air gaps. Cells are filled two-thirds, and then pollen is covered with honey to prevent spoilage.
Composition of Pollen
When discussing pollen composition, variations between different types must be considered. The quantity of each component depends on the plant species and flower size. Besides proteins, pollen contains numerous free amino acids, with 20-22 natural amino acids discovered, including eight essential for humans. A 100g serving of pollen equals the amino acid content of 500g of beef or seven eggs, meeting an adult’s daily protein needs. Key amino acids in pollen include arginine, histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, and methionine.
Pollen also contains water and carbohydrates (simple sugars glucose and fructose, and lactose) ranging from 35% to 40%. Fat content averages around 5%, with some types exceeding 20%. These fats are rich in unsaturated fatty acids that influence blood cholesterol levels. Additionally, pollen provides all essential vitamins, particularly B-group vitamins, A, C, biotin, and E, along with bioflavonoids, minerals, trace elements, enzymes, antibiotic substances, growth-promoting compounds, and rutin, strengthening capillary walls.
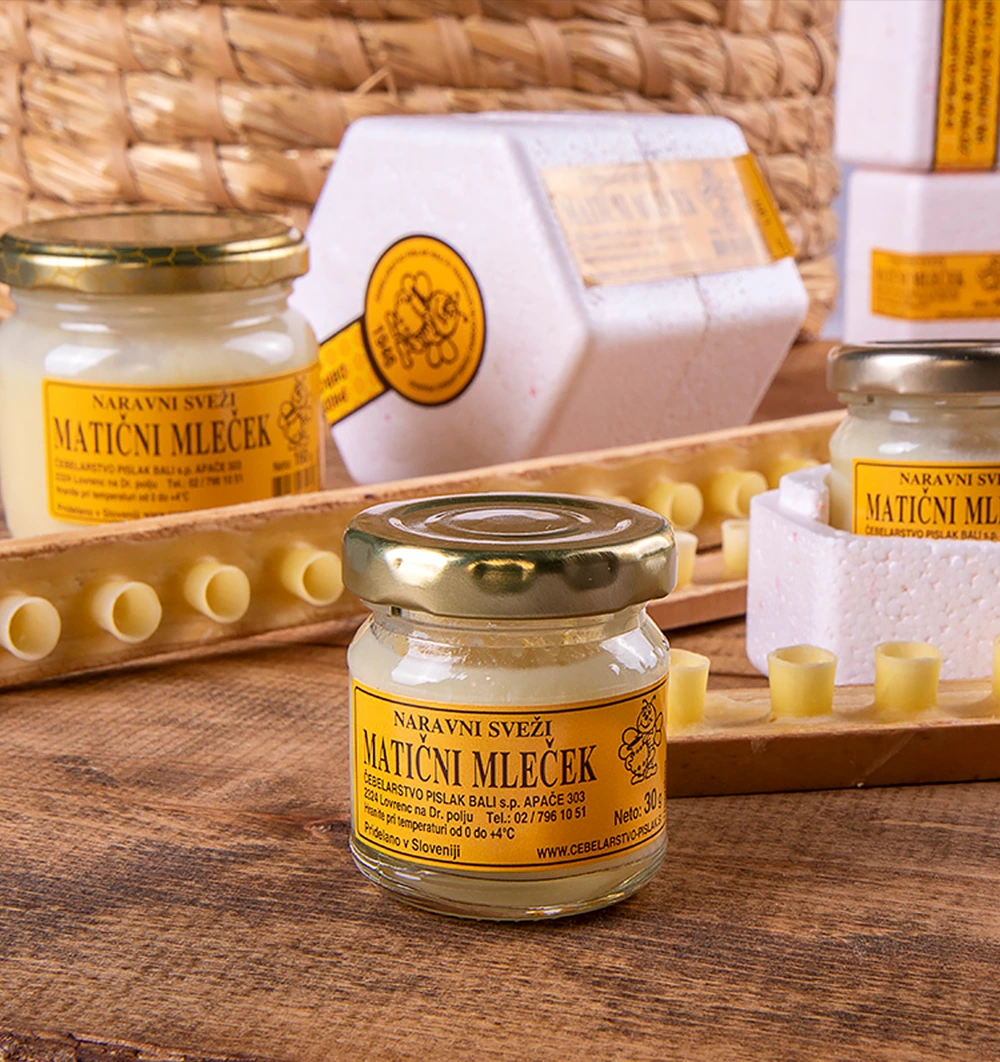
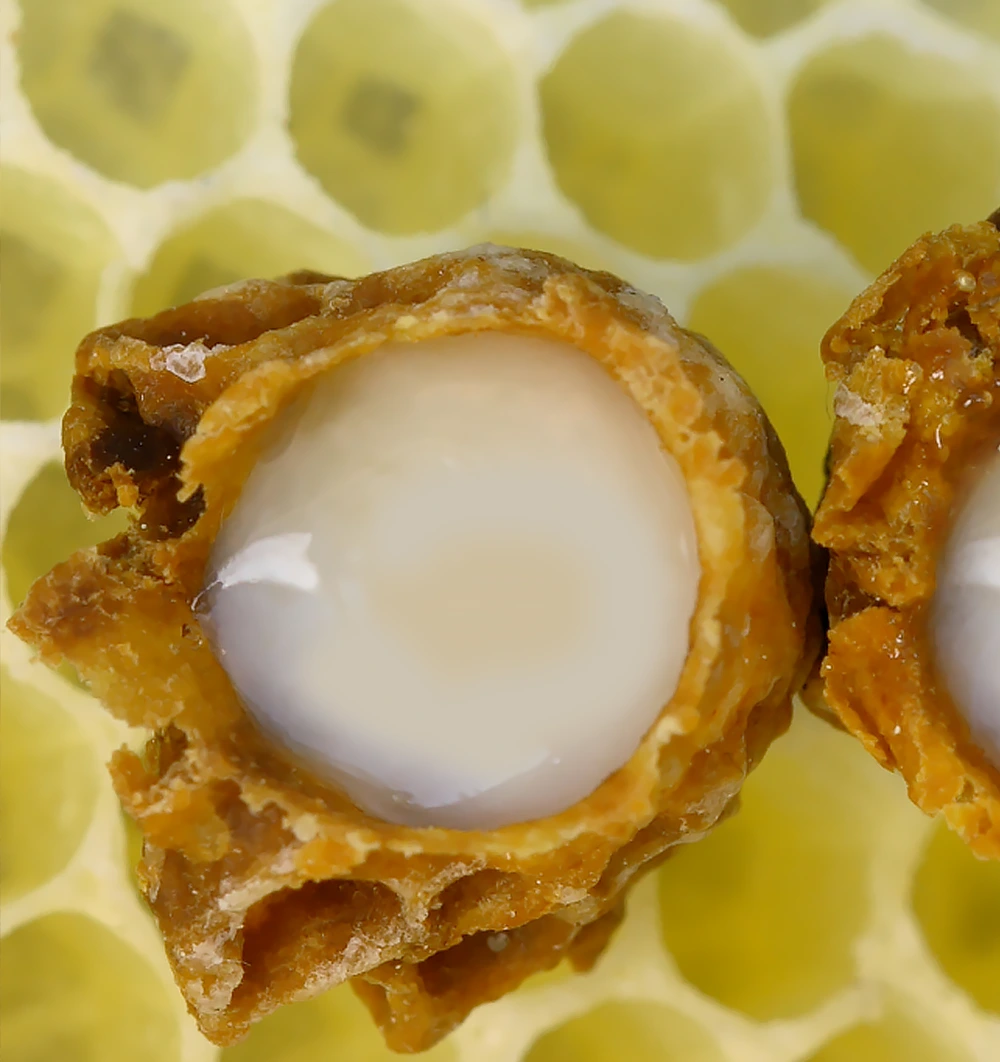
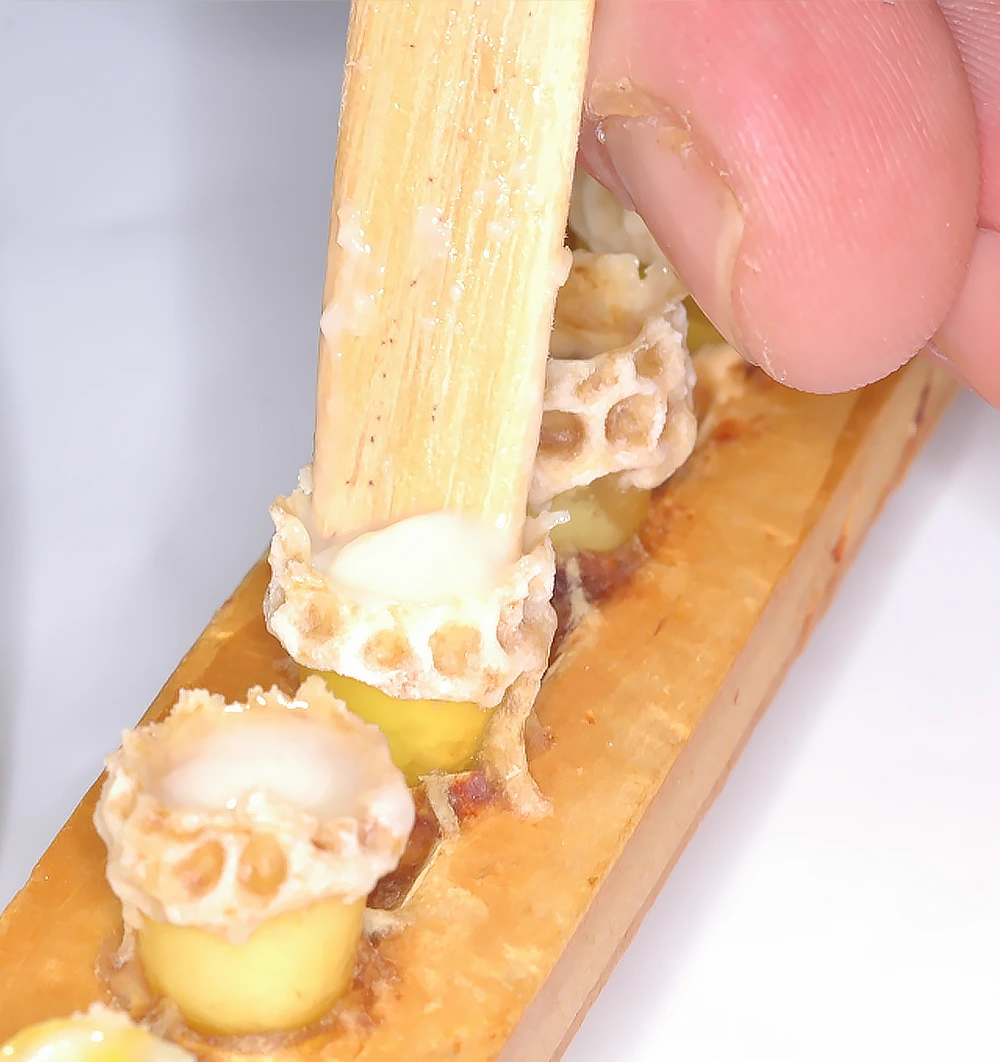



Healing Effects
Citrus Pollen: Suitable for calming nerves and considered a good stimulant. Also known to act as a remedy against intestinal parasites.
Chestnut Pollen: Effectively aids in treating varicose veins, increases red blood cell count, and reduces blood flow to the liver and prostate.
Eucalyptus Pollen: Disinfects and promotes mucus secretion. Effectively assists in colds, bronchitis, and elevated body temperature. Attributed antibacterial properties, influences stomach function, and aids in respiratory detoxification.
Lavender Pollen: Stimulates water elimination, soothes, and increases appetite.
Thyme Pollen: Disinfects, facilitates expectoration, effectively promotes blood circulation, and positively influences mental activity.
Buckwheat Pollen: Among the most important pollen types due to attributed medicinal properties. Contains rutin, a bioflavonoid that strengthens cell walls and blood vessels, aiding in preventing strokes and heart attacks.
Poppy Pollen: Assists with insomnia and nervousness. There are more types of pollen, but the listed ones are the most well-known.
Categorization of Pollen:
- Category 1: Chestnut, pear, white willow, white clover, strawberries, poppy, saffron, cereals.
- Category 2: Maple, beech, dandelion, sunflower, birch, corn.
- Category 3: Spruce, birch, hornbeam, pine, fir.
Functionality
Some scientists claim that due to its high protein and vitamin content, pollen successfully alleviates withdrawal symptoms in individuals recovering from alcohol dependence.
French doctor Chauvin studied pollen’s effects and found:
- Regulates bowel function, quickly stopping persistent diarrhea.
- Increased hemoglobin levels and noticeable improvement in overall well-being in anemic children.
- Rapid weight gain and regained strength in the elderly and convalescents.
- Stimulates appetite.
- Improves mood, reducing nervousness and irritability.
- Eases mental work, providing a slower, longer-lasting effect without harmful consequences.
- Enhances brain blood circulation. Russian researcher Deviatrein similarly demonstrated this.
Additional Benefits:
- Accelerates growth and improves vision.
- Works against hair loss due to the amino acid cystine in pollen, containing sulfur.
- Aids patients with prostate issues, as evidenced by Swedish doctor Upmark’s experiments treating acute urethral inflammation with pollen.
Inflammation Inhibition:
While pollen’s anti-inflammatory properties might be less known than other effects, a study at Gifu University (Japan) demonstrated this aspect. The study, conducted on rats, injected a substance causing inflammation (carrageenan). Rats then received pollen in various forms: dry pollen, water solution, ethanol solution, while a control group received nothing. Over 5 hours, swelling size was measured multiple times. While dry pollen was ineffective and the water solution almost had no effect, the ethanol solution exhibited a strong anti-inflammatory effect. Ethanol pollen solution significantly inhibited COX-2 (an enzyme responsible for inflammation) activity.
Allergies and Contraindications
During spring, when various pollen types are airborne, some people may experience more or less severe allergic issues. The pollen mentioned here, however, refers to entomophilous pollen collected by bees, not the windborne allergenic pollen. Allergic reactions may include symptoms such as allergic rhinitis (hay fever). Severe headaches, coughing, difficulty breathing, and irritability may also occur. Allergic reactions to ingesting pollen are rare but should prompt immediate discontinuation. Individuals with kidney disorders should limit or avoid pollen consumption, as the elimination of certain resins in pollen’s protective coating imposes an additional burden on the kidneys.
Other Uses
Effective for skin rejuvenation due to significant nucleic acid, vitamin, and mineral content.
Pollen Therapy
Best recommended during spring or seasonal changes. Start with one teaspoon on an empty stomach, gradually increasing to 15g (one tablespoon) after one week. After two weeks, two daily doses of 15g can be taken. To achieve desired effects, continue for at least one month. It’s advisable to repeat therapy several times a year, coinciding with seasonal changes, to ensure overall health.
Pollen represents the male reproductive cells of flowering plants. For bees, pollen, along with honey and water, constitutes their primary food.



Mnenja
Kaj drugi mislijo
Jaz sem ga jemala v postopku IVF in je bil rezultata zelo dober, sem pridelala 25 celic in potem od tega 13 zamrznjenih zarodkov. Mislim, da je folna kislina in matični mleček dovolj. Ni dobro, da preveč vsega naenkrat jemlješ. Upam, da nisi kupila matičnega mlečka v lekarni in da ga imaš od kakega čebelarja, so boljši. Jaz sem ga vzela vsak zvečer z plastično žličko. Na koničko žličke sem si ga zagrabila in pod jezik. Kdaj pa imaš punkcijo?
Matični mleček bi naj pozitivno deloval na neplodnost. Izkušnje žensk, ki dolgo niso mogle zanositi (seveda ob nepojasnjeni neplodnosti), so v roku 2 mesecev zanosile. Tudi sama sem ga nabavila za boljše celice pred ivf.
Pozdravljene! Zdaj že skoraj deset dni jem matični mleček in morama rečt, da se na okus nikakor ne morem navadit. Groza. Pa sploh nisem preveč občutljiva in vedno poskusim vse, ker me zanimajo okusi različnih stvari, ampak to mi pa nekako ne sede. Vedno moram imet nekaj zraven da poplaknem, ker me dobesedno dvigne. Ampak bom vztrajala in upala na pozitivne učinke.
Connections
PROVIDERS

ŠEMEN ŠTEFAN S.P. PRODAJA MEDU
Lipa 145 A
9231 Beltinci

ČEBELARSTVO LOVREC
Zlatoličje 95b
2205 Starše

ČEBELARSKI CENTER MARIBOR
TRGOVINA JANA
Jana Pušnik Pokrivač s.p.
Tavčarjeva 11, 2000 Maribor
ČEBELARSKI CENTER MARIBOR
Streliška 150, 2000 Maribor

MEDENI ZAKLAD D.O.O.
Serdica 17b
9262 Rogašovci
Počasi se pripravljam na IVF postopek,pa me zanima ali je katera od vas jemala matični mleček original od čebelarjev in kakšno dozo? Poleg tega pa jemljem še folno kislino… Ali je po vaše potrebno jemati še kaj za dobre celice in pripravo telesa na IVF? ŠE TO:matični mleček jemljem na žličko…je treba kar stisnit zobke…ta reč je res obupnega okusa.. ampak…vse za plusek…čau čau